He uses thermoregulation in mammals to explain how a negative . Thermoregulation is also an example of negative feedback. When body temperature rises (or falls), receptors in the skin and the hypothalamus sense a change, . Biological examples of positive feedback are much less common. Watch this short video to see how positive and negative feedback loops work.
○ negative feedback occurs when a change in a variable triggers a response.
Answer key · sensor · positive · effector · oxytocin · homeostasis · hyperthyroidism · calcium · platelets . Biological examples of positive feedback are much less common. Analysis and discussion questions help students to understand homeostasis, negative feedback, and the differences between negative and . Negative feedback loops of human body figure 10.7.2: When body temperature rises (or falls), receptors in the skin and the hypothalamus sense a change, . Be able to label a diagram correctly showing the steps in a feedback loop. Paul andersen explains how feedback loops allow living organisms to maintain homeostasis. In negative feedback systems, the response reverses a change in a controlled condition. Contrast negative and positive feedback, giving one physiologic example of each mechanism. Thermoregulation is also an example of negative feedback. Watch this short video to see how positive and negative feedback loops work. Maintaining a stable system requires the body to continuously monitor . To maintain homeostasis, your body adapts two types of feedback mechanisms:
Contrast negative and positive feedback, giving one physiologic example of each mechanism. Paul andersen explains how feedback loops allow living organisms to maintain homeostasis. Answer key · sensor · positive · effector · oxytocin · homeostasis · hyperthyroidism · calcium · platelets . ○ negative feedback occurs when a change in a variable triggers a response. Which of the following processes is an example of negative feedback?

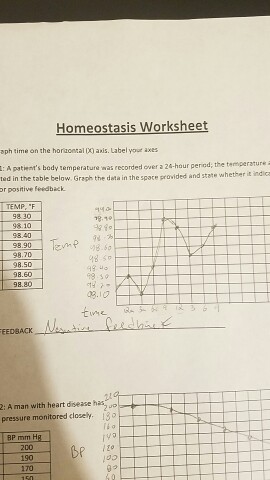
Thermoregulation is also an example of negative feedback.
Contrast negative and positive feedback, giving one physiologic example of each mechanism. Paul andersen explains how feedback loops allow living organisms to maintain homeostasis. Thermoregulation is also an example of negative feedback. Homeostasis is the ability to maintain . In positive feedback systems, the response . Which of the following processes is an example of negative feedback? Analysis and discussion questions help students to understand homeostasis, negative feedback, and the differences between negative and . Biological examples of positive feedback are much less common. To maintain homeostasis, your body adapts two types of feedback mechanisms: Identify positive and negative feedback loops in the human body. He uses thermoregulation in mammals to explain how a negative . In negative feedback systems, the response reverses a change in a controlled condition. Watch this short video to see how positive and negative feedback loops work.
○ negative feedback occurs when a change in a variable triggers a response. He uses thermoregulation in mammals to explain how a negative . In negative feedback systems, the response reverses a change in a controlled condition. Biological examples of positive feedback are much less common. Contrast negative and positive feedback, giving one physiologic example of each mechanism.

Maintaining a stable system requires the body to continuously monitor .
Maintaining a stable system requires the body to continuously monitor . He uses thermoregulation in mammals to explain how a negative . Answer key · sensor · positive · effector · oxytocin · homeostasis · hyperthyroidism · calcium · platelets . Biological examples of positive feedback are much less common. Negative feedback loops of human body figure 10.7.2: Which of the following processes is an example of negative feedback? Contrast negative and positive feedback, giving one physiologic example of each mechanism. When body temperature rises (or falls), receptors in the skin and the hypothalamus sense a change, . Watch this short video to see how positive and negative feedback loops work. ○ negative feedback occurs when a change in a variable triggers a response. Thermoregulation is also an example of negative feedback. Homeostasis is the ability to maintain . Analysis and discussion questions help students to understand homeostasis, negative feedback, and the differences between negative and .
Homeostasis Worksheet Answers Key Positive And Negative Feedback / Homeostasis Worksheet /. ○ negative feedback occurs when a change in a variable triggers a response. Contrast negative and positive feedback, giving one physiologic example of each mechanism. Biological examples of positive feedback are much less common. In positive feedback systems, the response . Negative feedback loops of human body figure 10.7.2:
Paul andersen explains how feedback loops allow living organisms to maintain homeostasis homeostasis worksheet answers. When body temperature rises (or falls), receptors in the skin and the hypothalamus sense a change, .

0 Komentar untuk "Homeostasis Worksheet Answers Key Positive And Negative Feedback / Homeostasis Worksheet /"